[OCT Observations] Optovue Solix Glaucoma Protocol
The SOLIX glaucoma package delivers in-depth analysis of the optic nerve head structure and vasculature. Optovue-exclusive scans bring additional insights that aid in clinical decision making.
Patient description
54-year-old Black female presented for comprehensive eye examination with complaints of blurry vision without her glasses. She was a Type 2 Diabetic of 6 years duration with very poor blood sugar control; her last HbA1C measured 11%. Her ocular history was positive for ocular hypertension. She had a positive family of glaucoma in a maternal aunt.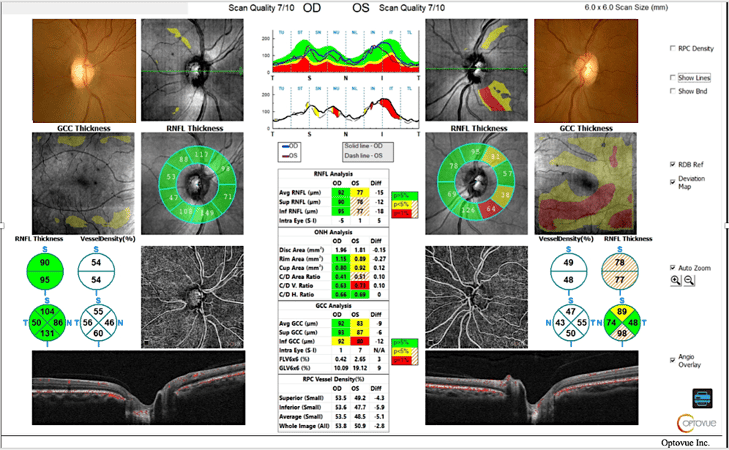
Clinical Findings
The patient’s intraocular pressure readings ranged from 22mmHg-29mmHg over the course of the last three years with a maximum IOP of 25mmHg OD and 29mmHg OS. Pachymetry measured 513 OD and 514 OS. Her optic nerve heads were pink and distinct with C/D ratios measuring .55V/.50H OD and .65V/.55H OS. Solix OCT Angiography was performed to further evaluate for the presence of glaucoma versus ocular hypertension.
Analysis of this patient’s right eye was unremarkable for the presence of glaucoma. Careful inspection of the left eye revealed thinning of the retinal nerve fiber layer inferior temporal and superior temporal to the optic nerve head. Quantitative data of the RNFL thickness corresponded with the thinning noted on the RDB map. Inspection of the tabular data shows a 15um difference in RNFL thickness and a 9um difference in GCC thickness between the right and left eyes. Of note is the large variation from the reference database in the ganglion cell thickness map of the left eye. These findings suggest that this patient may be at risk for developing glaucoma and further testing is warranted.
Conclusion
The Solix glaucoma package provides a comprehensive analysis of the optic nerve head including disc photos, retinal nerve fiber layer analysis, ganglion cell analysis, and vessel density metrics. A single scan generates both OCT and OCTA images with AngioAnalytics metrics to accurately identify damage to the radial peripapillary capillaries and track progression over time.
 Dr. Julie Rodman is the Chief of the Broward Eye Care Institute in Fort Lauderdale, FL and a Professor of Optometry at Nova Southeastern University. Her research interests include OCT/OCT-A and Vitreoretinal Disease. Dr. Rodman has authored over thirty publications with an emphasis on retinal disease. She recently published “Optical Coherence Tomography Atlas: A Case Study Approach,” the first reference book on this topic written by an optometrist. Dr. Rodman is a member of the AOA, AAO, FOA, and ORS. She has been the recipient of numerous teaching awards and was recognized as a Primary Care Optometry News “Top 300” Optometrists and “Newsweek Best Optometrists of 2021.”
Dr. Julie Rodman is the Chief of the Broward Eye Care Institute in Fort Lauderdale, FL and a Professor of Optometry at Nova Southeastern University. Her research interests include OCT/OCT-A and Vitreoretinal Disease. Dr. Rodman has authored over thirty publications with an emphasis on retinal disease. She recently published “Optical Coherence Tomography Atlas: A Case Study Approach,” the first reference book on this topic written by an optometrist. Dr. Rodman is a member of the AOA, AAO, FOA, and ORS. She has been the recipient of numerous teaching awards and was recognized as a Primary Care Optometry News “Top 300” Optometrists and “Newsweek Best Optometrists of 2021.”
The information is intended for general informational purposes only. It is not intended as, and should not be considered, a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment.
The content is not designed to replace the relationship that exists between a patient and their healthcare provider. Any medical decisions should be made in consultation with a qualified healthcare professional who can provide information tailored to your individual circumstances.
Medical procedures, case studies, and practices mentioned in this content may vary based on regional standards, local regulations, and the discretion of the providing healthcare professional. What may be considered appropriate and ethical in one country may differ in another.
The content may include general references to medical practices, medications, or treatments that are widely accepted in certain regions but may not be applicable or endorsed universally. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional in your jurisdiction to ensure the information is relevant to your specific situation.
The authors, publishers, and contributors of this content disclaim any liability for any adverse effects resulting directly or indirectly from information contained in this content. Readers should exercise their own judgment and seek the advice of healthcare professionals as appropriate.
By accessing and using this content, you acknowledge and agree to the terms of this disclaimer.